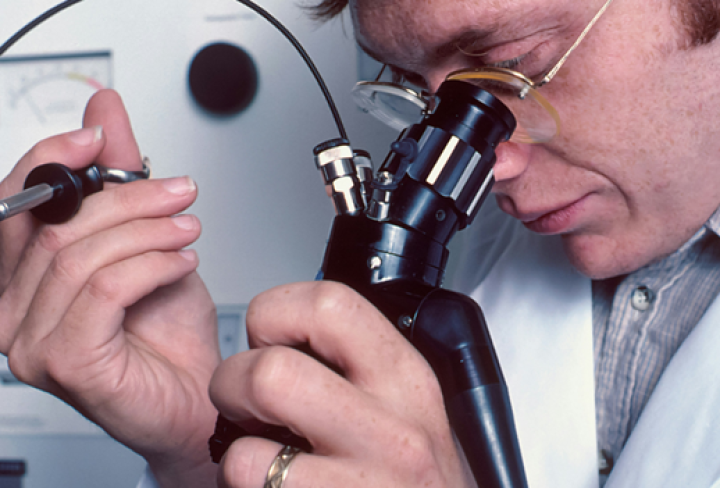
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy is a key tool doctors use to see inside the lungs and airways. Imagine having a tiny camera that can fit into the narrowest parts of the lungs. That’s what this device is like. It consists of a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light at the end.
This procedure helps doctors find and treat problems in the lungs or airways, like infections or blockages. It’s like a detective tool for finding out what’s wrong when someone is having trouble breathing. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedures play an important role by providing clear images and helping doctors understand a person’s lung health.
Understanding this procedure is vital for anyone dealing with breathing issues. It’s less scary if you know what happens during the process. This guide aims to make this procedure easier to understand and explain why it’s important. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy techniques are quite advanced and allow for high-quality diagnostics, helping in early detection and treatment.
Overall, this technique is very helpful in maintaining healthy lungs. It allows for both a thorough examination and even some treatments during the same appointment. By exploring the insides of the airways, doctors can catch problems before they get serious.
Understanding the Procedure: Preparation, Execution, and Experience
Preparing for a fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedure means following a few simple rules. Before the test, doctors usually ask you not to eat or drink for several hours. This ensures your stomach is empty, which makes the procedure safer. Your doctor might also tell you to stop taking certain medicines temporarily.
When you arrive at the hospital or clinic, you’ll meet the healthcare team who will guide you. They will explain what to expect and check if you have any allergies or health concerns. Then, they might use a numbing spray in your nose or throat to make you more comfortable.
During the procedure, the doctor gently inserts the bronchoscope through the nose or mouth. It moves carefully down the throat into the lungs. You might feel slight pressure or the urge to cough, but it’s normally not painful. Healthcare providers ensure patients feel at ease during this step. They closely watch your breathing and help you remain calm.
Here’s what usually happens in a few simple steps: 1. Preparation: No food or drinks beforehand, and the doctor gives you instructions. 2. During the Procedure: The bronchoscope goes through the nose or mouth. 3. Support: Healthcare providers guide you and keep you safe.
After it’s done, you might feel sleepy, especially if medication was used to help relax you. Most people can go home after a few hours. The doctor talks with you about what they found and what the next steps might be.
Risks, Complications, and How It Compares to Other Techniques
Like any procedure, fiberoptic bronchoscopy does come with some risks. The most common ones are mild. You might have a sore throat, a small risk of infection, or slight bleeding. However, doctors are trained to manage these and keep you safe.
For comparison, there’s another similar procedure called rigid bronchoscopy. It uses a more solid tube instead of a flexible one. This often requires general anesthesia, meaning you’re fully asleep. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy anesthesia is less intense, usually involving just a mild sedative to relax you.
Understanding the difference between these methods can help guide your healthcare choices. The complications of fiberoptic bronchoscopy are generally fewer compared to its rigid counterpart, making it a gentler option for patients.
By knowing these differences: – Less Invasive: Fiberoptic bronchoscopy is easier on the body. – Flexible Equipment: It can navigate tight spaces better. – Less Anesthesia: It usually doesn’t require you to be completely asleep.
With these advantages, fiberoptic bronchoscopy indications are clear—it’s preferred when needing a detailed look inside the lungs with minimal discomfort.
The Value and Advantages of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy
The uses of fiberoptic bronchoscopy make it a standout in diagnosing lung problems. One significant advantage is it doesn’t require heavy anesthesia. You stay awake, often aware of the process but relaxed, while still reaping its benefits.
The tool gives doctors a real-time view inside, which means they can see problems right away. If needed, they can even perform minor treatments on the spot. This dual capacity to diagnose and treat is a major reason why it’s so valuable to doctors.
Key advantages include: – No General Anesthesia: It reduces risks and recovery time. – Quick Response: Doctors can act on findings immediately. – Efficient Diagnosis: Real-time imaging supports accurate assessments.
In choosing between fiberoptic bronchoscopy vs rigid bronchoscopy, the flexible option often wins. Its ability to check and address issues swiftly makes it ideal for many situations. It offers a comprehensive approach, allowing doctors to take biopsies or remove small obstructions right away.
Overall, fiberoptic bronchoscopy holds a crucial place in medical practices. It’s gentle yet effective, helping protect our lungs by quickly finding and addressing concerns. Whether you’re preparing for one or simply wanting to learn more, understanding this method’s value helps in making informed health choices.