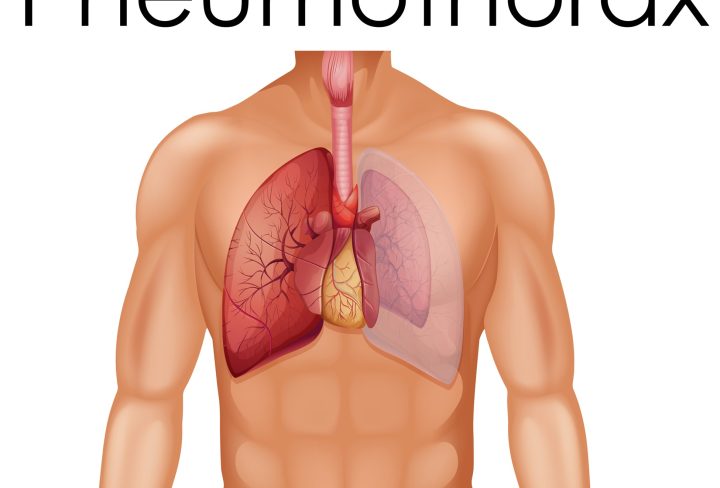
A pneumothorax happens when air escapes into the space between your lung and chest wall. This unexpected event causes your lung to collapse either fully or partially. When this happens, you might feel sudden, sharp chest pain and have trouble breathing. There are different types of pneumothorax: spontaneous, traumatic, or iatrogenic. Each type has its own set of explanations and risks. Recognizing the symptoms of pneumothorax and understanding the causes of pneumothorax early on is key. It makes getting the right treatment easier and helps you avoid more serious health issues.
In this blog, we aim to share information about pneumothorax—its symptoms, causes, and how it can be treated. This way, you can be more prepared and knowledgeable should you encounter this condition.
Spotting the Symptoms and Uncovering the Causes of Pneumothorax
When a pneumothorax occurs, it comes with some clear signs:
- You might feel a stabbing pain in your chest.
- Breathing could become a real challenge.
- You could notice a rapid heartbeat.
- Having low blood pressure might leave you feeling weak or dizzy.
It’s important to understand that a spontaneous pneumothorax typically happens due to lung issues you might already have or when small air sacs, called blebs, burst in your lungs. Knowing who is more at risk can help in preventing it from happening to you. Things like smoking or existing lung conditions increase your chances. Of course, stopping smoking or managing lung health better can reduce these odds.
Then there’s the traumatic pneumothorax, which is usually due to an accident or injury. Lastly, we have the iatrogenic kind, which might occur after certain medical procedures. Each of these types needs to be recognized properly to ensure the right care is given.
Having a basic understanding of these symptoms of pneumothorax and causes can make a big difference. You’re more likely to seek help faster or guide someone else to do so.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pneumothorax: Ensuring Effective Management and Prevention
Understanding how pneumothorax is diagnosed and treated helps you face it confidently. To diagnose this condition, doctors rely on:
- Physical exams to feel and listen to your chest for abnormalities.
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, to see how much air is outside your lungs.
- Blood tests to check how well oxygen is reaching your organs.
When managing a pneumothorax, treatment will vary based on its severity:
- Monitoring: In minor cases, if your symptoms are not severe, doctors might choose to observe and wait for your lung to re-inflate naturally.
- Needle Aspiration: This is a simple way to remove extra air from the chest area done by inserting a needle and drawing out the air.
- Chest Tube Insertion: A bit more involved than needle aspiration, a chest tube helps continuously remove air, allowing your lung to expand over time.
- Surgery: For more severe or recurring cases, doctors might recommend surgery to repair the lung and prevent future issues.
Aside from dealing with a pneumothorax when it happens, prevention matters a lot too. You can:
- Quit smoking. This alone can reduce the risk dramatically.
- Avoid risky activities like diving, where pressure changes can impact your lungs.
- Follow through with medical advice, especially if you have chronic lung problems.
While pneumothorax sounds quite serious, managing it effectively is possible with proper care and attention to its signs. Keeping in mind the simple lifestyle changes can make all the difference in preventing another episode.
It is also helpful to note the difference between pneumothorax vs pleural effusion. While they might sound alike, they’re quite different. Pneumothorax involves air in the chest cavity, while pleural effusion involves fluid. This distinction is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Pneumothorax in children might differ slightly. Children can be more expressive about discomfort, but it poses a different challenge to identify non-verbally observed signs. If your child shows unusual breathing patterns or complains of chest pain, it’s essential to seek medical advice quickly.
By exploring these themes there is a deeper understanding of pneumothorax and its management. With knowledge, you can address the condition more calmly and effectively.