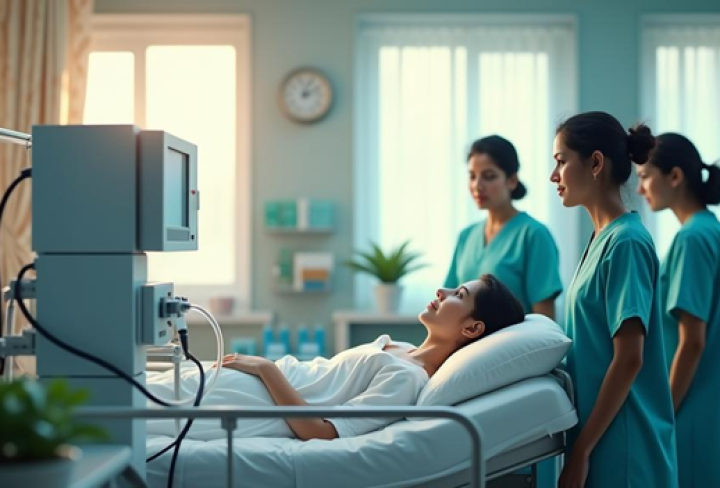
Ventilators are lifesaving machines crucial in healthcare, particularly during respiratory crises. Their importance skyrocketed during the COVID-19 crisis, as hospitals needed them to help patients breathe. Understanding how ventilators work is vital because it highlights their role in critical health scenarios.
Learning about ventilators removes fear and uncertainty. Often, people fear things they do not understand, including medical devices. By understanding how a medical ventilator works, anxiety decreases, replacing it with confidence in recovery processes. This knowledge builds trust in healthcare systems across communities.
Ventilators step in for patients unable to breathe independently, providing essential oxygen. They are especially important in intensive care units where their function can decide outcomes. Special training is needed to use ventilators effectively in hospitals, reflecting their sophisticated design. While complex, ventilators primarily stabilize patients—offering crucial support during precarious times.
Understanding Medical Ventilators: Terminology and Concepts
Understanding medical ventilators is vital when exploring how hospitals manage patient care. Let’s decipher some common terms:
- PEEP keeps your airways open after you breathe out, assisting lung function.
- FiO2 is about controlling how much oxygen you receive, tailored to needs.
- Tidal Volume is the air sent into your lungs each breath, carefully adjusted.
Mechanical ventilation helps people who struggle to breathe by mimicking natural processes. In simple terms, it provides oxygen and removes carbon dioxide when normal breathing fails. Ventilators play a crucial role for patients requiring this life-saving support in hospitals, especially in critical care situations.
Ventilators are built from key parts that work harmoniously:
- The Air Compressor ensures there’s a steady flow of air to your lungs.
- Sensors keep track of how well your breathing works and inform doctors.
- Control Systems coordinate when you inhale or exhale, ensuring you stay safe.
Different Modes of Ventilation and Their Uses
Ventilators offer two main modes of breathing assistance: controlled and spontaneous. In controlled mode, the machine takes control, helping those who can’t breathe alone. Meanwhile, spontaneous mode assists patients who can start their own breaths but need extra help maintaining it. This mode supports natural breathing efforts while ensuring adequate airflow.
Volume Control Mode delivers a specific air volume with each breath, ensuring consistent lung filling. This approach is vital during surgeries or severe crises where exact air volumes are essential. Doctors set the volume as needed, making the method adaptable for various situations while maintaining the patient’s stability.
Pressure Control Mode manages pressure within the lungs for those with sensitive lung tissue. By focusing on pressure limits, this technique reduces the risk of further damage and provides gentle respiratory support. Doctors often choose this approach when safeguards against high pressures are more important than precise volumes.
The question “how does a medical ventilator work” ties into these modes, aiding in understanding their specific applications in hospital settings.
The Weaning Process: Transitioning Patients from Ventilators
The weaning process from ventilators is like teaching your body to breathe naturally again. Gradually reducing ventilator dependence helps muscles regain their strength, step by step. As patients improve, this approach allows them to regain their natural breathing capability.
Before starting the ventilator weaning process, several essential factors are checked. First, clinicians assess if the patient’s condition remains stable over time. Next, they ensure breathing muscles possess enough strength to function independently. It is also vital that patients should be conscious and response-ready throughout. Furthermore, medical staff perform regular tests like spontaneous breathing assays to determine readiness.
In the process of weaning off a ventilator, medical teams are crucial. They monitor progress daily and adjust ventilator settings as needed. Providing emotional support to both patients and families throughout this challenging transition is paramount. This teamwork helps align with care protocols that aim at prioritizing patient safety and health progress.
Dispelling Myths: Common Misconceptions About Ventilators
Many people think patients stay on ventilators forever, but that’s not true. Often, ventilators are used for short periods to help patients recover better. Doctors follow a careful plan to help patients stop using ventilators when they’re ready. This plan is personal, not one-size-fits-all, mostly offering temporary help when needed.
Some think ventilators do all the breathing for patients, creating worry. Ventilators support natural breathing when lungs can’t efficiently exchange air by themselves. With oxygen supply, these machines help respiratory systems work better even during tough times, easing the body’s workload.
Knowing how ventilators work in hospitals helps ease public fears. Ventilators are crucial for recovery from illnesses harming breathing, already lessening worry by spreading knowledge. Awareness prompts sensible talks about medical devices, helps families decide wisely about care, and proves ventilator use is well-managed by skilled healthcare providers.